From Liquid to Gas: Understanding the Different Forms of Nitrogen Supplied by Wigmore Trading
From Liquid to Gas: Understanding the Different Forms of Nitrogen Supplied by Wigmore Trading
Welcome to the fascinating world of nitrogen! Nitrogen is an essential element for life as we know it, and understanding its various forms is crucial in many industries. Today, we are diving into the topic of nitrogen supply with Wigmore Trading – a leading provider of industrial gases. From liquid to gas, they offer a range of nitrogen options that cater to different needs and applications. Whether you’re curious about cryogenic liquids or high-pressure cylinders, this blog post will unravel the mysteries behind these diverse forms and help you make informed decisions for your business. So buckle up as we embark on a journey through the transformational states of nitrogen supplied by none other than Wigmore Trading!
Introduction to Nitrogen and its Uses
Nitrogen is a chemical element with the symbol N and atomic number 7. It is a colorless, odorless, and tasteless gas that makes up around 78% of Earth’s atmosphere. Although it is the most abundant gas in the air we breathe, pure nitrogen gas (N2) is not readily available for use in its gaseous state. Instead, it must be extracted from other sources such as liquid or solid compounds.
In its natural state, nitrogen exists as a diatomic molecule, meaning two nitrogen atoms bonded together to form N2. This strong bond between the two atoms makes it difficult to separate them and use nitrogen in its gaseous form. However, through various processes such as fractional distillation or membrane separation, pure nitrogen can be obtained from air or other sources.
One of the main uses of gaseous nitrogen is in industrial applications. Due to its inert properties (meaning it does not react with other substances), it is commonly used as a blanketing agent to prevent oxidation or spoilage of food products during packaging and storage. It also plays an important role in preventing explosions by displacing oxygen in industrial environments where flammable materials are present.
Another significant application of gaseous nitrogen is in the production of fertilizers for agriculture. Nitrogen gas can be converted into ammonia (NH3) through a process called Haber-Bosch synthesis and then further processed into different types of fertilizers that provide essential nutrients for plant growth.
Understanding the Different Forms of Nitrogen: Liquid vs Gas
Nitrogen is an essential element for life on Earth and plays a crucial role in various industries. It is the most abundant gas in our atmosphere, making up about 78% of the air we breathe. However, nitrogen can also exist in other forms, namely liquid and solid. In this section, we will delve deeper into the two different forms of nitrogen – liquid and gas – to understand their properties, uses, and supply methods.
Liquid Nitrogen:
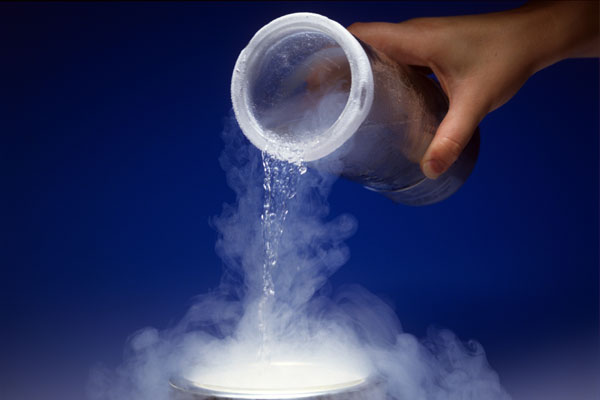
Liquid nitrogen (LN2) is a colorless and odorless cryogenic liquid with a boiling point of -195.8°C (-320°F). It is produced by cooling gaseous nitrogen to extremely low temperatures through a process called liquefaction. LN2 has several unique properties that make it valuable for various applications.
One of the most notable properties of LN2 is its extremely low temperature. At such low temperatures, materials become brittle and can be easily shattered or fractured. This property makes LN2 ideal for cryogenic freezing applications, where delicate biological samples or electronic components need to be preserved without any damage.
Another significant property of LN2 is its ability to rapidly evaporate upon exposure to ambient temperature. When exposed to room temperature, LN2 quickly turns into gas and expands at around 700 times its original volume. This process is known as boil-off or vaporization, which creates pressure within closed containers that store LN2. Therefore, proper handling procedures must be followed while dealing with liquid nitrogen to prevent potential hazards.
The Production Process of Liquid and Gas Nitrogen
The production process of liquid and gas nitrogen involves many complex steps and requires advanced technology to ensure the highest quality of the final product. In this section, we will delve into the production process of both forms of nitrogen – liquid and gas – to gain a better understanding of how they are produced.
Liquid Nitrogen Production Process:
The first step in producing liquid nitrogen is obtaining pure nitrogen gas from the atmosphere. This can be done through either cryogenic air separation or pressure swing adsorption (PSA). Cryogenic air separation involves cooling air until it liquefies, then separating it into its different components based on their boiling points. Nitrogen has a lower boiling point than oxygen, allowing for its separation in this process.
Once pure nitrogen gas is obtained, it is further cooled and compressed until it reaches a temperature below -320°F (-196°C), at which point it turns into a liquid state. The resulting liquid nitrogen is then stored in insulated containers to maintain its extremely low temperature.
One crucial aspect of the production process for liquid nitrogen is maintaining its purity. Even small amounts of impurities can affect its properties and potentially pose safety hazards. Therefore, strict quality control measures are implemented throughout every stage of production.
Gas Nitrogen Production Process:
The production process for gas nitrogen also begins with obtaining pure nitrogen from the atmosphere using cryogenic air separation or PSA technology. However, instead of being cooled to a liquid state, the resulting pure nitrogen gas undergoes compression to increase its pressure.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Liquid and Gas Nitrogen
Advantages of Liquid Nitrogen:
1. Efficient Cooling: Liquid nitrogen has a very low boiling point of -196°C, making it an extremely efficient coolant. It can quickly cool down objects and materials to ultra-low temperatures, making it ideal for industrial processes such as cryogenic freezing.
2. Easy Storage and Transportation: Unlike compressed gas nitrogen, liquid nitrogen takes up much less space during storage and transportation. This makes it easier to handle and transport in large quantities, reducing costs for businesses.
3. Versatility: Liquid nitrogen has a wide range of applications in various industries such as food processing, pharmaceuticals, aerospace, and research laboratories. It can be used for freezing, cooling, inerting, and preserving materials without any chemical contamination.
4. Non-toxic and Environmentally Friendly: Nitrogen is a naturally occurring element that is non-toxic and does not pose any harm to the environment when used correctly. Liquid nitrogen also evaporates quickly into the atmosphere without leaving any residue or harmful by-products.
5. Cost-effective: In comparison to other cooling methods like dry ice or refrigeration systems, liquid nitrogen is more cost-effective due to its low energy consumption and maintenance costs.
Disadvantages of Liquid Nitrogen:
1. Handling Hazards: While liquid nitrogen is considered safe when handled properly with appropriate protective gear, it can cause severe frostbite if it comes into contact with skin or eyes. The extreme cold temperature can also damage certain materials if not handled carefully.
Applications of Liquid and Gas Nitrogen in Various Industries
Nitrogen is an essential element that plays a crucial role in many industries. From food preservation to medical procedures, this versatile gas has numerous applications. However, nitrogen can exist in two different forms: liquid and gas. While both forms have similar properties and uses, they are supplied and used differently depending on the industry’s needs.
In this section, we will discuss the various applications of liquid and gas nitrogen in different industries.
1. Food Industry
One of the most common uses of liquid nitrogen in the food industry is for cryogenic freezing and chilling. Liquid nitrogen has a boiling point of -320°F (-195°C), making it extremely cold. This extreme temperature allows it to freeze food quickly, preserving its freshness and texture better than traditional freezing methods. Moreover, liquid nitrogen is also used for creating frozen desserts like ice cream, as it can instantly freeze the ingredients while keeping them smooth and creamy.
Gas nitrogen is often used for packaging foods such as chips or nuts to prevent oxidation and extend their shelf life. It creates a protective atmosphere around the packaged food by displacing oxygen, which helps slow down spoilage caused by exposure to air.
2. Medical Industry
Both liquid and gas nitrogen have important applications in the medical industry. In its liquid form, nitrogen is commonly used for cryosurgery – a procedure that involves using extreme cold temperatures to destroy abnormal tissues such as skin tags or warts.
How Wigmore Trading Supplies Nitrogen in Nigeria and Worldwide
Wigmore Trading is a leading supplier of nitrogen in Nigeria and around the world. Nitrogen is an essential element used in various industries such as manufacturing, food processing, and medical fields. As a gas, nitrogen is widely used for its non-reactive properties which make it suitable for many applications. In this section, we will explore how Wigmore Trading supplies nitrogen and the different forms it comes in.
1. Liquid Nitrogen Supply:
One of the main ways Wigmore Trading supplies nitrogen is in its liquid form. Liquid nitrogen has a boiling point of -195.8°C making it extremely cold and efficient for many industrial processes. It is stored at very low temperatures in specialized tanks to keep it in its liquid state.
Wigmore Trading sources high-quality liquid nitrogen from reputable manufacturers to ensure that our clients receive pure and reliable products. We have a fleet of specially designed trucks that are equipped with cryogenic tanks to transport liquid nitrogen safely to our customers’ locations.
2. Compressed Gas Supply:
Another form of nitrogen supplied by Wigmore Trading is compressed gas. This type of supply comes in cylinders or tanks filled with compressed nitrogen gas at high pressure. Unlike liquid nitrogen, compressed gas does not require specialized storage facilities but still needs to be handled with care due to its high-pressure nature.
Wigmore Trading offers various sizes of cylinders and tanks depending on our customer’s requirements, from small portable cylinders to large bulk tanks for continuous supply.
Partnering with Reputable Producers for High-Quality Nitrogen Supply
At Wigmore Trading, we pride ourselves on providing our customers with the highest quality nitrogen supply. We understand that having a reliable and consistent source of nitrogen is crucial for many industries, which is why we have partnered with reputable producers to ensure that our customers receive nothing but the best.
When it comes to industrial gases, such as nitrogen, it is important to work with trusted producers who adhere to strict quality standards. This not only ensures the purity and safety of the gas but also guarantees its effectiveness in various applications.
One of our trusted partners is Air Products, a leading global supplier of industrial gases. Their state-of-the-art facilities and expertise in gas production allow us to offer a wide range of high-quality nitrogen products. From liquid nitrogen for cryogenic applications to gaseous nitrogen for purging and inerting processes, Air Products delivers exceptional purity and reliability.
In addition to Air Products, we also collaborate with other renowned producers such as Linde Gas and Praxair. These partnerships allow us to expand our product offerings and cater to a diverse range of industries including food packaging, pharmaceuticals, electronics manufacturing, oil and gas, and more.
What sets these producers apart from others in the market is their commitment to sustainability. They have implemented advanced technologies in their production processes that reduce energy consumption and emissions while ensuring maximum efficiency. This aligns with Wigmore Trading’s values of promoting environmentally responsible practices within the industry.
Safety Measures for Handling Liquid and Gas Nitrogen
When it comes to handling liquid and gas nitrogen, safety should always be the top priority. Nitrogen is a colorless, odorless, and tasteless gas that can pose serious health hazards if not handled properly. In this section, we will discuss the necessary safety measures that should be taken when handling both liquid and gas nitrogen.
1. Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
The first step in ensuring safety when handling nitrogen is wearing appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE). This includes gloves made of materials such as neoprene or nitrile, face shields or safety goggles, and a lab coat or apron. These PPEs act as a barrier between the skin and any potential exposure to liquid or gas nitrogen.
2. Proper Storage
It is important to store liquid nitrogen in well-ventilated areas with minimal exposure to direct sunlight. The storage area should also be secure and away from any sources of heat or open flames as liquid nitrogen can evaporate rapidly at room temperature, causing an increase in pressure within sealed containers.
3. Proper Handling Techniques
Liquid nitrogen should only be transferred using approved containers specifically designed for cryogenic liquids. When transferring liquid nitrogen from one container to another, use vacuum-jacketed hoses with built-in filters to prevent any potential splashing or spilling of the extremely cold liquid.







Comments are closed.